|
Pigeon Diseases, Symptoms and Treatment (The most common pigeon diseases) |
|||
|
Paratyphoid |
Candida | Paramyxovirus | Canker |
| Coccidiosis | Ornithosis |
Adeno-Coli Syndrome |
|
|
Some of these diseases are viral, some bacterial and also parasitic. Pigeon diseases symptoms can give us clear hints of Pigeon diseases. Normal pigeon sickness can be cure by pigeon medicine but some Pigeon diseases effects are deadly and even proper pigeon treatments cannot save your bird’s life. To keep well your pigeon health please treat them good, make a healthy hygienic nest for adult homing pigeons and baby pigeons and watch Pigeon Diseases symptoms. |
|||
|
Paratyphoid Pigeon Disease |
|
Paratyphoid Disease Description and Symptoms: Gram-negative Salmonella bacillus bacteria cause the Paratyphoid disease. To be more exact, in pigeons that is the Salmonella var. Copenhagen. The disease can be expressed in clinical and subclinical (latent) form. In the latent form of the disease, the symptoms are not showing very well or not at all and the pigeon’s performance is mediocre. As in the clinical form of the disease, there are several symptoms that are well recognizable. The pigeons lose weight, and their general condition is getting worse, the droppings are slimy and green, their legs and wing joints are swollen, they limp, their eggs are infertile, they sometimes twist their neck on the side and sometimes they go blind on one eye. There is acute form of the disease and chronic form. The acute form occurs in pigeons that have never been vaccinated or infected with the salmonella bacteria and they don’t have any immunity against the disease. The pigeons have diarrhea, sometimes even bloody. They drink less to no water at all and they get dehydrated. This can end in death because of dehydration. In the chronic form of the disease, the more common one, the disease spreads in the internal organs: gut, liver, kidneys, reproductive system, and spleen. Sometimes the bacteria can cause arthritis and nervous symptoms. The symptoms in the chronic form are not so clear. There are problems in the reproduction, the eggs cannot be hatched, and there is loss of appetite and weight. |
| Paratyphoid Disease Diagnosis: The diagnosis can be sometimes difficult because a lot of times the tests can be false negative. The mean is the disease is present but the tests on salmonella negative. The tests are done on collected droppings for five consecutive days. Another way for diagnosing the disease is autopsy of pigeons that are suspected to be ill. Also determining antibodies in blood samples is done as diagnostic procedure but this way only recently infected pigeons can be diagnosed. |
|
Paratyphoid Disease Prevention and treatment: There are vaccines and antibiotics available, however they are both not 100{6be2db3b88870d4886eebf8b9afca4bb83e0a042bc3cf1b41260af04e7c2bfbe} sure. Because even if the pigeons are cured from the disease, they remain carriers of the bacteria. The most effective antibiotic is Enrofloxacine. The vaccine treatment can be with live and dead vaccines and some pigeon keepers can even make auto-vaccines. The most effective are probably the live vaccines. However, the vaccinating schedule is very important in prevention and treatment of the disease and it varies depending on the vaccine. The place where the pigeons are kept should be cleaned regularly, disinfected and the hygiene should be good. |
|
Candida Pigeon Disease |
|
Candida Disease Description and Symptoms: This disease is caused by the yeast Candida albicans. This is normally present in the digestive system of the pigeons. Sometimes its increases and causes damage and problems in the digestive tract, the respiratory system, and the beak, also it can infect the skin, eyes, feathers, reproductive system. Symptoms of the disease are poor growth of young pigeons, whitish fungal growths in the throat and accumulation in the crop. |
| Candida Disease Diagnosis: For diagnosing this disease, the fungal growths in the throat should be examined microscopically. |
|
Candida Disease Prevention and Treatment: For preventing the disease, the environment needs to be improved, regarding the hygiene. As for treatment, the affected pigeons need to be separated and treated with Nystatin and Vitamin A. |
|
Paramyxovirus Pigeon Disease |
|
Paramyxovirus Disease Description and Symptoms: This virus is highly pathogen for pigeons. There is clinical and subclinical form of the disease. In both cases, the virus is spread through secretions from the nose, throat, conjunctiva and the droppings. Symptoms of the disease are increased water intake, reduced appetite, diarrhea and polyuria, paralysis of the legs, twisting of the body and the neck and walking backwards. |
| Paramyxovirus Disease Diagnosis: The disease can be diagnosed in several ways; autopsy, serological examination of blood samples taken from suspicious pigeons. |
|
Paramyxovirus Disease Prevention and Treatment: Like any other viral disease, there is no treatment for affected pigeons. Those Pigeons should be removed from the flock. Sometimes affected pigeons can recover spontaneously after 4 weeks of illness. However if there is suspicion of the disease, an emergency vaccination should be done in order to prevent infecting the healthy pigeons. Multivitamin EB12 is recommended to give to the pigeons. For prevention, there is active immunization, after which the pigeons develop stable immunity. |
|
Canker Pigeon Disease |
|
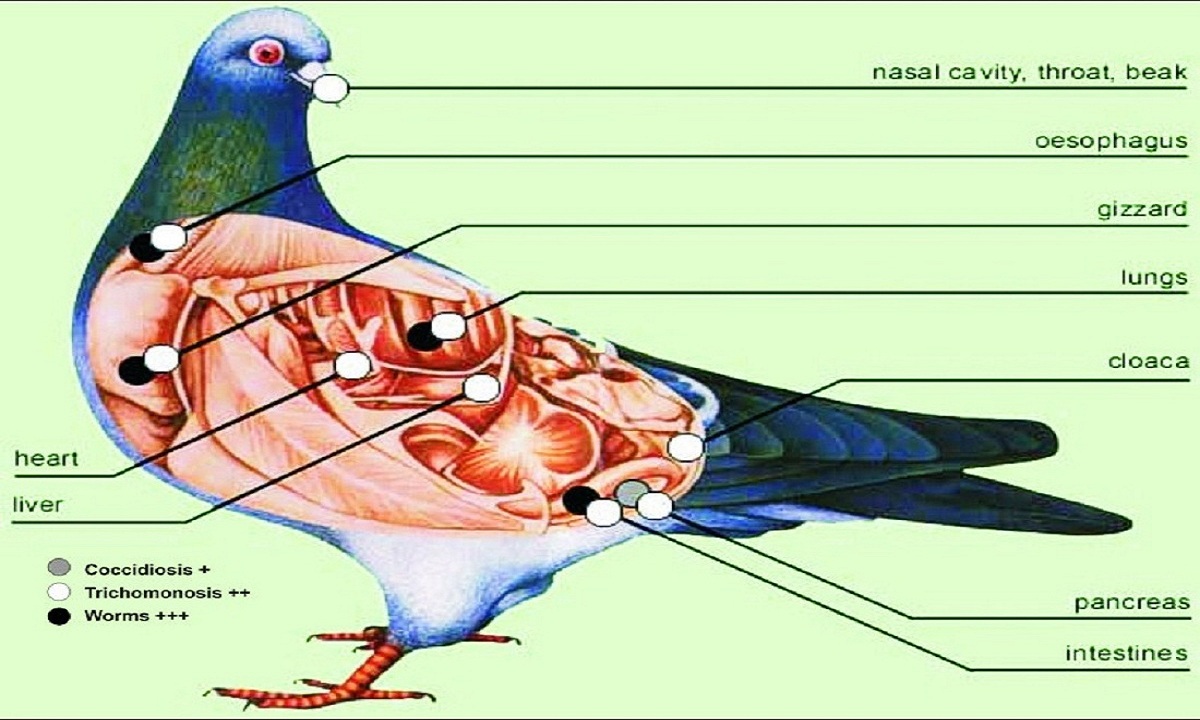
Canker Disease Description and Symptoms: Canker is Also called Trichomoniasis. This is a very common disease among pigeons, even more among racing pigeons. The disease affects most of the pigeons during their lifetime but symptoms are rarely presented in mature birds. However when the birds are stressed that is a trigger for symptoms such as losing weight, looking ruffled to show up. If not treated the birds soon die. Other symptoms that occur are: repeated swallowing movements, ruffled plumage and apathy, yellow stuff in the throat and on the beak, increased water intake, weight loss and weakness. Usually healthy pigeons get this disease while they are transported with other ill pigeons. Because they all drink water from the same place. The disease can be in several forms, pharyngeal form is the most common one. it is distinguished for the yellow stuff in the throat of the bird, umbilical canker, is canker that passes to the birds in the nest from the infected pigeon; organ form. When the canker attacks the internal organs, like the liver, most birds die in this case from liver failure. |
|
Canker Disease Prevention and Treatment: For treating this disease, Ronidazole is the suggested drug and the most used one. It is important to know that pigeons that have this disease cannot swallow, so they could die from starvation. In that case, they have to be fed with Critical Care Formula, which is put in the water, and International Rehydration Solution made by mixing 1 pint warm water with half a dessert spoon of honey or sugar mixed in and half a teaspoon of salt. |
|
Coccidiosis Pigeon Disease |
|
Coccidiosis Disease Description and Symptoms: Coccidiosis is a very common disease among pigeons and it is highly infectious. It is caused by a protozoan that attacks the intestines. The most affected group of pigeons is the young ones. Some pigeons that were subjected to stress; as for the adult ones, they usually have developed immunity to the disease but they can become infected after drinking infected water or being in contact with droppings from infected birds. This disease presents itself through various symptoms, such as: loss of appetite, no desire to drink water, the pigeons do not move and they close their eyes, they are puffed up, their droppings are greenish and watery, they lose weight. As it is a parasitic disease, it is good to know how it attacks the system. An infected organism releases eggs in the droppings. These eggs become infective after few days, even quicker if the environment is damp. After this when a healthy pigeon accidentally swallows infective eggs, they move in the intestines and hatch. Four larvae come out of every egg and they continue to reproduce asexually in the wall if the intestines. Later they differentiate in males and females and continue reproducing sexually, which results in eggs. Those eggs go in the environment in the droppings and the cycle continues. |
| Coccidiosis Disease Diagnosis: If you suspect the disease is present, the droppings should examine under microscope by a veterinarian. |
| Coccidiosis Disease Prevention and Treatment: In order to prevent Coccidiosis, the place where the pigeons are kept should be clean and dry. The drinkers should be disinfected regularly and the food must not come in contact with the droppings. Also new birds should be isolated for several weeks before they are put together with other birds. There are several treatments to consider, such as giving Toltrazuril or Sulphur antibiotics or Amprolium. |
|
Ornithosis Pigeon Disease |
|
Ornithosis Disease Description and Symptoms: Ornithosis is a very important disease because it can spread to humans and other animals. It is caused by Chlamydia psittaci, which are small microorganisms that invade the cells parasitically. Healthy birds can become infected by inhalation of dust that contains the pathogen, intake of contaminated water or food. There are two forms of the disease, acute form and chronic form. The acute form has symptoms such as: conjunctivitis, wheezing noises, muco-aqueous enteritis and diarrhea. The chronic form is frequently found in adult birds but it shows little to no symptoms. Recovered pigeons are a source of infection due to their latent phase of shedding the pathogen. |
| Ornithosis Disease Diagnosis: The disease can be diagnosed by microscopic examination of a smear or impression preparation of liver, spleen, and conjunctiva. This is done with dead birds. In live birds, serological blood tests can be done; also examination of the feces can be used as a diagnostic method. |
|
Ornithosis Disease Prevention and Treatment: For treatment Doxycycline-T should be used for 25 days treatment period. For prevention a resistance drink can be used. |
|
Adeno-coli syndrome Pigeon Disease |
|
Adeno-coli syndrome Disease Description and Symptoms: The pathogens that cause this disease are the adenovirus and the E. coli bacterium. This disease usually occurs in young birds but recently is found out that even older birds can be affected. Stress and poor living conditions are triggers of the syndrome. As for symptoms they are well known, such as poor appetite, excessive drinking, watery diarrhea, vomiting. In addition there is weight loss and the disease can spread in 48h in the whole loft. After the birds are infected with the adenovirus, the disease gets complicated with the E. coli contamination. E. coli can weaken the birds and the droppings are green and foul smelling. This disease causes damage to the liver, the intestines and birds can even die from liver failure. |
| Adeno-coli syndrome Disease Diagnosis: The diagnosis can be based on the clinical signs and symptoms but to be sure, the level of E. coli should be examined |
|
Adeno-coli syndrome Disease Prevention and Treatment: To prevent this disease, the hygiene in the loft should be optimal. Also stress should be reduced; the drinkers and feeders should be disinfected regularly. For treating the disease, the E.coli should be brought down to optimum, and the adenovirus should be treated as well. |
IAM VERY MUCH GRAEFUL WIH THIS INFORMATION , I ALSO PRAY THAT YU CONTINUE TO GIVE ME MORE INFORMATION ON HOW TO TAKE CARE OF MY PIGEONS SO THAT THEY REMAIN HEALTHY AND PRODUCTIVE THANK YOU VERY MUCH AND BEST REGARDS TO YOU.